Pain Behind The Knee: Learn to Identify The Causes of Your Knee Pain
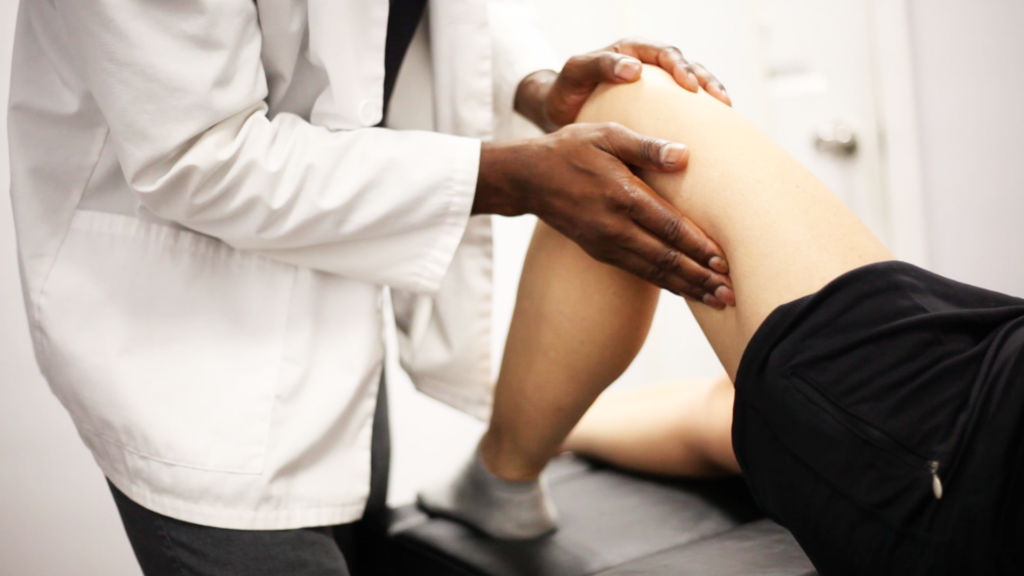
Table of Contents
TogglePain Behind The Knee: Learn to Identify The Causes of Your Knee Pain
Have you been experiencing chronic pain behind the knee that doesn’t go away? This may be a sign that you are injured!
Pain in the back of the knee is very common. The knee is the biggest joint in the body and this is why it is one of the most injury-prone structures. This type of knee pain can be triggered by multiple conditions, the vast majority of which are injury-related.
In today’s blog, we will take a closer look at six major injuries and conditions that might lead to back-of-knee pain. We will talk about causes, symptoms and treatment options for each injury.
Let’s begin!
Baker’s Cyst
The first cause for pain behind the knee is a Baker’s cyst or popliteal cyst.
A Baker’s cyst is an inflammation of the bursa located behind the knee. As a consequence, a fluid-filled cyst forms causing a bulge and a feeling of tightness in the area.
A Baker’s cyst is usually due to an underlying injury in the knee joint such as arthritis or a cartilage tear. This condition may increase the production of fluids in the knee. A Baker’s cyst will appear when the body is unable to naturally eliminate the excess of fluid in the knee joint.
Symptoms
Baker’s cysts can be very painful for some patients. It can even affect their ability to perform daily activities. In other cases, it causes no pain and the patient may not notice their condition at all. However, If you do have signs and symptoms they might include:
- Swelling behind the knee and leg
- Knee pain
- Stiffness
- Inability to fully flex the knee
Treatment
An effective therapy for a Baker’s cyst focuses on treating the underlying cause of the injury. This is the only way to provide pain relief to the area. Ideally, treatment would include a combination all of the following therapies: acupuncture, chiropractic care, physiotherapy and massage therapy.
A visit to a chiropractor is highly recommended. Joint mobilizations can assist improving the movement around the knee joint. Physiotherapy will work on stretching and strengthening the muscles below and above surrounding the knee joint as well. This is very important to gain knee stability.
On the other hand, massage therapy can help to decrease the swelling, eliminate excess fluids, and work on relaxing the muscles below and above the affected area.
Lastly, acupuncture sends signals to the brain in order to increase blood flow to the knee. Acupuncture needles would be placed in various points around the knee. The main goal would be decrease pain, decrease swelling, and subsequently, allowing for proper movement without restriction.
We recommend a holistic well rounded treatment for Baker’s cysts as each practitioner can focus on rehabilitating a different aspect of your knee.
Biceps Femoris Tendinitis
Another common cause of pain at the back of the knee is biceps femoris tendinitis or simply known as a hamstring strain. This is an inflammation, or more likely a degeneration of the hamstring tendon at the point where it attaches to the back of the knee.
The biceps femoris alongside with the semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles are used to strongly bend the knee and extend the hip backward. Hamstring strains can occur from a partial rupture that has not healed properly or through overuse of this tendon, particularly from accelerating and decelerating activities.
This injury is frequent in patients participating in specific sports that require athletes to run fast such as soccer, tennis, and track and field.
Symptoms
Biceps femoris tendinitis pain is gradual pain and it appears on the outside/back of the knee. Other symptoms may include:
- Visible bruising
- Inflammation
- Weakness in the back of the legs
- Trouble moving the leg
- Pain when trying to bend the knee against resistance
- Stiffness after exercise
Treatment
Hamstring strains can be very debilitating. If left undiagnosed and untreated, it can lead to prolonged pain at the back of the knee and a prolonged lay-off from exercise and sports.
Physiotherapy is crucial when this condition. Physiotherapy will not only focus on helping strengthen the weak biceps femoris muscle, but also to strengthen all the hamstrings and some of the muscles below the knee. This is very important for proper healing.
Moreover, chiropractic joint mobilizations rehabilitate overall movement in the area. This will result in the patient having a better range of motion in the joint.
Finally, massage therapy can help decrease pain and swelling in the hamstring.
Remember, the key thing here is to really rehabilitate the hamstrings and get them stronger.
Gastrocnemius tendinitis
The next condition we are going to talk about is called gastrocnemius tendinitis or a calf strain. Just like biceps femoris tendinitis, gastrocnemius tendinitis is an inflammation or degeneration of the tendon of the calf muscle resulting in pain at the back of the knee.
The muscle we commonly referred as the calf is actually called the gastrocnemius muscle. The upper end of this muscle attaches on the back of the knee, while the lower end inserts onto the back of the heel via the Achilles’ Tendon.
The gastrocnemius is an important ankle and knee muscle, and plays a principal role in maintaining proper mechanics at the knee with weight bearing activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs.
Symptoms
When the calf muscle gets pulled it causes sudden pain, visible bruising behind the knee, there could be swelling, and trouble standing on the toes. Other symptoms may include:
- Gradual tightness on the back knee
- Pain on the inside or outside of the knee depending on the injury
- Reduced ankle’s range of motion
- Pain may worsen and be present during activity
Treatments
Gastrocnemius tendinitis treatment involves three mayor components: reducing the pain, decreasing inflammation and full rehabilitation.
First, an exercise program will be designed to restore the muscle and tendon function. This is going to be the main goal.
Secondly, we supplement the exercise program with chiropractic joint mobilizations, assisted physiotherapy stretching and strengthening exercises to repair the injured muscle, and massage therapy to relax the area to decrease bruising and any swelling in the knee joint.
Meniscus Tear
A meniscal tear is one of the most frequent injuries that occur in the cartilage of the knee. It can be extremely painful and very debilitating.
There are two menisci that are located on the knee on the medial and lateral side. These two pieces of cartilage act as shock absorbers between your thighbone and shinbone.
A torn meniscus occurs when there is trauma in this area caused by forceful twisting or hyper-flexing of the knee.
Symptoms
Most common symptoms include:
- Pain in the back of the knee
- Swelling
- A popping sensation at the time of injury
- Difficulty bending and straightening the leg
- A tendency for the knee to lock up
Treatments
Treatment for meniscus tears mainly depends on the size and location of the tear. Other factors that influence how a treatment is designed include age of the patient, activity level and other related injuries.
Recommended therapies include chiropractic care to help unlock the knee, to strengthen surrounding muscles, and to improve overall range of motion of the joint.
Massage therapy helps decrease pain and inflammation by working on the muscles below and above the knee joint.
Lastly, physiotherapy focuses on rehabilitating the surrounding area including the quadriceps, the calves, and the front of the leg in order to get the knee more stable.
Additionally, acupuncture points around the knee and into the knee joint to help blood flow in the area has been shown to be effective with decreasing pain and achieving higher range of motion in that knee joint.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury
The next cause of pain could be due to an injury in the posterior cruciate ligament. This is the ligament runs across the back of the knee and connects the thighbone to the shinbone.
Although it is larger and stronger ligament than the anterior cruciate ligament, the posterior cruciate ligament can be torn very easily. In fact, these tears make up almost 20% of all injuries to knee ligaments.
Moreover, tears in the posterior cruciate often damage some of the other ligaments or cartilage in the knee. There is also a high risk that the ligament breaks loose a piece of underlying bone.
Posterior cruciate ligament injuries are often due to a blow to the front of the knee while it’s bent. This could happen during a car accident, slip and fall, or by playing sports such as soccer, football, or skiing.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms include:
- Swelling (mild to severe)
- Stiffness
- Knee pain
- Restriction with flexion
- Sometimes visible bruising if it is severe
- Wobbly sensation in the knee
- Trouble walking or bearing weight on the knee
Treatments
Rehabilitation plays a vital role in getting you back to your daily activities. A physical therapy program will be customized to your lifestyle to help you regain knee strength and motion.
Non surgical treatments options include RICE method. Even at home you should practice the RICE principles when dealing with posterior cruciate ligament injury.
Professional services recommended include chiropractic joint mobilizations to improve range of motion in the joint, physiotherapy to help strengthen and stretch all the leg muscles that support the knee, massage therapy to help decrease any swelling, bruising and any tight muscles in the knee joint, and acupuncture, specifically behind the knee, and to increase blood flow to the area.
A therapeutic knee bracing will be recommend to prevent your knee from moving.
One key note to remember is that although it is a slow process of recovery, your commitment to therapy is the most important factor in returning to all the activities you enjoy. If left untreated, a posterior cruciate ligament injuries tear can lead to osteoarthritis in the knee.
Chondromalacia patellae
The last cause for pain behind the knee we are going to cover is a condition called chondromalacia patellae or runner’s knee.
It occurs when the cartilage inside the patella or kneecap deteriorates, softens, and breaks down either due to arthritis, overuse, repetitive injuries or just ageing.
The risk of developing chondromalacia patella increases when there is abnormal kneecap positioning, tightness or weakness in the muscles surrounding the knee, deterioration of the knee structure due to overuse, and flat feet.
Improper kneecap movement may result from:
- Poor alignment due to a congenital condition
- Weak hamstrings and quadriceps
- Muscle imbalance between the adductors and abductors
- Repeated stress to your knee joints
- Repetitive motions in athletes involved in running, skiing, or jumping
- Direct blow or trauma to the kneecap
Symptoms
Usually, there is a dull ache behind the kneecap, overall weakness in the knee joint, trouble with movement, knee instability, and the pain may get worse when climbing up the stairs.
It is very important to pay special attention to any feeling of grinding when the knee is flexed. This can happen while doing knee bends, going down stairs, running down hill, or standing up after sitting for a while.
Treatments
The primary goal for rehabilitation of chondromalacia patella is to change the way the kneecap is moving into a straighter pathway to follow during quadriceps contraction.
Patients must seek guided physical therapy for knee instability. This will help the inner portion of the quadriceps muscles get the knee properly stable.
At this point, knee brace may be recommended to maintain the kneecap aligned properly. Additionally, treatment should be complemented with at home ice therapy right above the knee or on the knee joint for about 15 to 20 minutes daily.
Patients must avoiding high-impact exercises, all kneeling and squatting.
Unlike other conditions we have covered in this blog, if the cartilage has been damaged, surgery is usually required.
What to do next…
If you feel that you are suffering from any of these conditions that may be causing pain behind the knee, please make sure to get a thorough a proper and thorough assessment to find the root cause of the problem.
You can always give us a call or contact us through our website and we can give you more information.
How Can PhysioChiroWellness Help?
At PhysioChiroWellness Integrated Health Centre our highly skilled practitioners work together to create fully integrated health solutions that may include physiotherapy, chiropractic, massage therapy, acupuncture, naturopathy, medical aesthetics amongst others. Our professionals will work together towards achieving an optimal health for all our patients through a holistically approach when treating any condition or pain they may present. This service is provided in our Ajax, Mississauga, Newmarket, & Vaughan clinics and can be booked at any `time.
